第15页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
10. 如图,在Rt△ABC中,∠ACB = 90°,BC = 3,AC = 4,AB的垂直平分线DE交BC的延长线于点E,则CE的长为 ( )
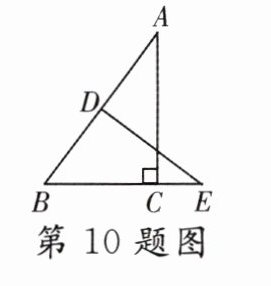
A. $\frac{3}{2}$
B. $\frac{7}{6}$
C. $\frac{25}{6}$
D. 2

A. $\frac{3}{2}$
B. $\frac{7}{6}$
C. $\frac{25}{6}$
D. 2
答案:
B
11. 如图,等腰三角形ABC的底边BC长为4,面积是18,腰AC的垂直平分线EF分别交AC,AB边于E,F点. 若点D为BC边的中点,点G为线段EF上一动点,则△CDG的周长的最小值为______.
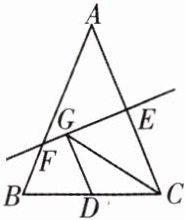

答案:
11 【解析】连接$AD$,$\because\triangle ABC$是等腰三角形,点$D$是$BC$边的中点,$\therefore AD\perp BC$. $\therefore S_{\triangle ABC}=\frac{1}{2}BC\cdot AD=\frac{1}{2}\times4AD = 18$. 解得$AD = 9$. $\because EF$是线段$AC$的垂直平分线,$\therefore$点$C$关于直线$EF$的对称点为点$A$. $\therefore AD$的长为$CG + GD$的最小值. $\therefore\triangle CDG$的周长的最小值$=(CG + GD)+CD = AD+\frac{1}{2}BC = 9+\frac{1}{2}\times4 = 11$.
解得$AD = 9$. $\because EF$是线段$AC$的垂直平分线,$\therefore$点$C$关于直线$EF$的对称点为点$A$. $\therefore AD$的长为$CG + GD$的最小值. $\therefore\triangle CDG$的周长的最小值$=(CG + GD)+CD = AD+\frac{1}{2}BC = 9+\frac{1}{2}\times4 = 11$.
11 【解析】连接$AD$,$\because\triangle ABC$是等腰三角形,点$D$是$BC$边的中点,$\therefore AD\perp BC$. $\therefore S_{\triangle ABC}=\frac{1}{2}BC\cdot AD=\frac{1}{2}\times4AD = 18$.
 解得$AD = 9$. $\because EF$是线段$AC$的垂直平分线,$\therefore$点$C$关于直线$EF$的对称点为点$A$. $\therefore AD$的长为$CG + GD$的最小值. $\therefore\triangle CDG$的周长的最小值$=(CG + GD)+CD = AD+\frac{1}{2}BC = 9+\frac{1}{2}\times4 = 11$.
解得$AD = 9$. $\because EF$是线段$AC$的垂直平分线,$\therefore$点$C$关于直线$EF$的对称点为点$A$. $\therefore AD$的长为$CG + GD$的最小值. $\therefore\triangle CDG$的周长的最小值$=(CG + GD)+CD = AD+\frac{1}{2}BC = 9+\frac{1}{2}\times4 = 11$. 12. 如图,∠A = ∠D = 90°,AB = DC,点E,F在直线BC上,且BE = CF.
(1)求证:∠E = ∠F.
(2)若PO平分∠EPF,则PO与线段BC有什么关系?为什么?
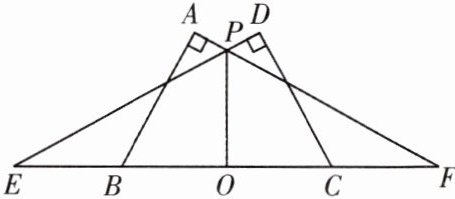
(1)求证:∠E = ∠F.
(2)若PO平分∠EPF,则PO与线段BC有什么关系?为什么?

答案:
(1) 证明:$\because BE = CF$,$BC = CB$,$\therefore BF = CE$. 在$Rt\triangle ABF$与$Rt\triangle DCE$中,$\begin{cases}BF = CE\\AB = DC\end{cases}$,$\therefore Rt\triangle ABF\cong Rt\triangle DCE(HL)$. $\therefore \angle E=\angle F$.
(2) 解:$PO$垂直平分线段$BC$. 理由:由
(1)可知,$\angle E=\angle F$. $\therefore\triangle PEF$为等腰三角形. 又$\because PO$平分$\angle EPF$,$\therefore PO\perp BC$,$EO = FO$. 又$\because EB = FC$,$\therefore BO = CO$. $\therefore PO$垂直平分线段$BC$.
(1) 证明:$\because BE = CF$,$BC = CB$,$\therefore BF = CE$. 在$Rt\triangle ABF$与$Rt\triangle DCE$中,$\begin{cases}BF = CE\\AB = DC\end{cases}$,$\therefore Rt\triangle ABF\cong Rt\triangle DCE(HL)$. $\therefore \angle E=\angle F$.
(2) 解:$PO$垂直平分线段$BC$. 理由:由
(1)可知,$\angle E=\angle F$. $\therefore\triangle PEF$为等腰三角形. 又$\because PO$平分$\angle EPF$,$\therefore PO\perp BC$,$EO = FO$. 又$\because EB = FC$,$\therefore BO = CO$. $\therefore PO$垂直平分线段$BC$.
13. 定义:到三角形的两个顶点距离相等的点,叫做此三角形的准外心.
举例:如图1,若PA = PB,则点P为△ABC的准外心.
应用:如图2,CD为等边三角形ABC的高,准外心P在高CD上,且PD = $\frac{1}{2}$AB,求∠APB的度数.
探究:已知△ABC为直角三角形,斜边BC = 5,AB = 3,准外心P在AC边上,试探究PA的长.
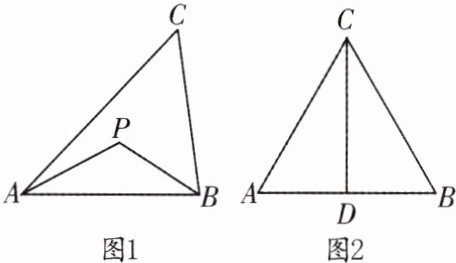
举例:如图1,若PA = PB,则点P为△ABC的准外心.
应用:如图2,CD为等边三角形ABC的高,准外心P在高CD上,且PD = $\frac{1}{2}$AB,求∠APB的度数.
探究:已知△ABC为直角三角形,斜边BC = 5,AB = 3,准外心P在AC边上,试探究PA的长.

答案:
解:应用:①若$PB = PC$,连接$PB$,则$\angle PCB=\angle PBC$,$\because CD$为等边三角形的高,$\therefore AD = BD$,$\angle PCB = 30^{\circ}$. $\therefore \angle PBD=\angle PBC = 30^{\circ}$. $\therefore PD=\frac{1}{2}PB$. $\therefore DB=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}PB$. $\therefore PD=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}DB=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{6}AB$,与$PD=\frac{1}{2}AB$矛盾,$\therefore PB\neq PC$.
②若$PA = PC$,连接$PA$,同理可得$PA\neq PC$.
③若$PA = PB$,由$PD=\frac{1}{2}AB$,得$PD = BD$,$\therefore \angle APD = 45^{\circ}$,故$\angle APB = 90^{\circ}$.
探究:$\because BC = 5$,$AB = 3$,$\therefore AC=\sqrt{BC^{2}-AB^{2}}=\sqrt{5^{2}-3^{2}} = 4$.
①若$PB = PC$,设$PA = x$,则$x^{2}+3^{2}=(4 - x)^{2}$,$\therefore x=\frac{7}{8}$,即$PA=\frac{7}{8}$.
②若$PA = PC$,则$PA = 2$.
③由图知,在$Rt\triangle PAB$中,$PB>PA$,$\therefore PA\neq PB$.
 综上所述,$PA = 2$或$\frac{7}{8}$.
综上所述,$PA = 2$或$\frac{7}{8}$.
解:应用:①若$PB = PC$,连接$PB$,则$\angle PCB=\angle PBC$,$\because CD$为等边三角形的高,$\therefore AD = BD$,$\angle PCB = 30^{\circ}$. $\therefore \angle PBD=\angle PBC = 30^{\circ}$. $\therefore PD=\frac{1}{2}PB$. $\therefore DB=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}PB$. $\therefore PD=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}DB=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{6}AB$,与$PD=\frac{1}{2}AB$矛盾,$\therefore PB\neq PC$.
②若$PA = PC$,连接$PA$,同理可得$PA\neq PC$.
③若$PA = PB$,由$PD=\frac{1}{2}AB$,得$PD = BD$,$\therefore \angle APD = 45^{\circ}$,故$\angle APB = 90^{\circ}$.
探究:$\because BC = 5$,$AB = 3$,$\therefore AC=\sqrt{BC^{2}-AB^{2}}=\sqrt{5^{2}-3^{2}} = 4$.
①若$PB = PC$,设$PA = x$,则$x^{2}+3^{2}=(4 - x)^{2}$,$\therefore x=\frac{7}{8}$,即$PA=\frac{7}{8}$.
②若$PA = PC$,则$PA = 2$.
③由图知,在$Rt\triangle PAB$中,$PB>PA$,$\therefore PA\neq PB$.
 综上所述,$PA = 2$或$\frac{7}{8}$.
综上所述,$PA = 2$或$\frac{7}{8}$. 查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


