第56页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
例3 如图,在△ABC中,CD⊥AB,BE⊥AC,$\frac{DE}{BC}$ = $\frac{2}{5}$,则sin A的值为( )
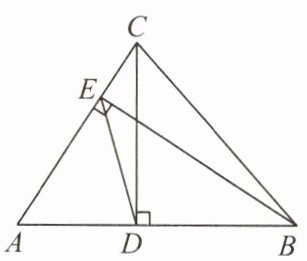
A. $\frac{2}{5}$
B. $\frac{\sqrt{21}}{5}$
C. $\frac{\sqrt{21}}{2}$
D. $\frac{3}{5}$

A. $\frac{2}{5}$
B. $\frac{\sqrt{21}}{5}$
C. $\frac{\sqrt{21}}{2}$
D. $\frac{3}{5}$
答案:
B
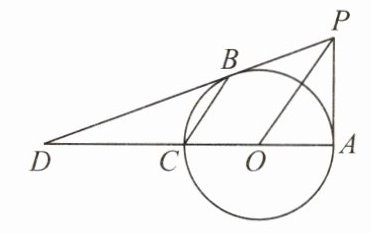
3. 如图,AC是⊙O的直径,PA⊥AC,连接OP,弦CB//OP,直线PB交直线AC于点D,BD = 2PA.
(1) 求证:直线PB是⊙O的切线;
(2) 探究线段PO与线段BC之间的数量关系,并加以证明;
(3) 求sin∠OPA的值.
(1) 求证:直线PB是⊙O的切线;
(2) 探究线段PO与线段BC之间的数量关系,并加以证明;
(3) 求sin∠OPA的值.

答案:
(1) 连接 $OB$,如图. $\because BC// OP$,$\therefore \angle BCO=\angle POA$,$\angle CBO=\angle POB$, $\therefore \angle POA=\angle POB$, 又 $\because PO = PO$,$OB = OA$, $\therefore \triangle POB\cong\triangle POA$. $\therefore \angle PBO=\angle PAO = 90^{\circ}$. $\therefore PB$ 是 $\odot O$ 的切线.
(2) $2PO = 3BC$. $\because \triangle POB\cong\triangle POA$,$\therefore PB = PA$. $\because BD = 2PA$,$\therefore BD = 2PB$. $\because BC// PO$,$\therefore \triangle DBC\sim\triangle DPO$. $\therefore \frac{BC}{PO}=\frac{BD}{PD}=\frac{2}{3}$,$\therefore 2PO = 3BC$.
(3) $\because \triangle DBC\sim\triangle DPO$, $\therefore \frac{DC}{DO}=\frac{BD}{PD}=\frac{2}{3}$, 即 $DC=\frac{2}{3}OD$. $\therefore OC=\frac{1}{3}OD$, $\therefore DC = 2OC$. 设 $OA = x$,$PA = y$. 则 $OD = 3x$,$OB = x$,$BD = 2y$. 在 $Rt\triangle OBD$ 中,由勾股定理得 $(3x)^{2}=x^{2}+(2y)^{2}$,即 $2x^{2}=y^{2}$. $\because x>0$,$y>0$,$\therefore y=\sqrt{2}x$,$OP=\sqrt{x^{2}+y^{2}}=\sqrt{3}x$. $\therefore \sin\angle OPA=\frac{OA}{OP}=\frac{x}{\sqrt{3}x}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}$.

(1) 连接 $OB$,如图. $\because BC// OP$,$\therefore \angle BCO=\angle POA$,$\angle CBO=\angle POB$, $\therefore \angle POA=\angle POB$, 又 $\because PO = PO$,$OB = OA$, $\therefore \triangle POB\cong\triangle POA$. $\therefore \angle PBO=\angle PAO = 90^{\circ}$. $\therefore PB$ 是 $\odot O$ 的切线.
(2) $2PO = 3BC$. $\because \triangle POB\cong\triangle POA$,$\therefore PB = PA$. $\because BD = 2PA$,$\therefore BD = 2PB$. $\because BC// PO$,$\therefore \triangle DBC\sim\triangle DPO$. $\therefore \frac{BC}{PO}=\frac{BD}{PD}=\frac{2}{3}$,$\therefore 2PO = 3BC$.
(3) $\because \triangle DBC\sim\triangle DPO$, $\therefore \frac{DC}{DO}=\frac{BD}{PD}=\frac{2}{3}$, 即 $DC=\frac{2}{3}OD$. $\therefore OC=\frac{1}{3}OD$, $\therefore DC = 2OC$. 设 $OA = x$,$PA = y$. 则 $OD = 3x$,$OB = x$,$BD = 2y$. 在 $Rt\triangle OBD$ 中,由勾股定理得 $(3x)^{2}=x^{2}+(2y)^{2}$,即 $2x^{2}=y^{2}$. $\because x>0$,$y>0$,$\therefore y=\sqrt{2}x$,$OP=\sqrt{x^{2}+y^{2}}=\sqrt{3}x$. $\therefore \sin\angle OPA=\frac{OA}{OP}=\frac{x}{\sqrt{3}x}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}$.

例4 如图,线段AB是⊙O的直径,弦CD⊥AB于点H,M是$\overset{\frown}{CBD}$上任意一点,AH = 2,CH = 4,求sin∠CMD的值.
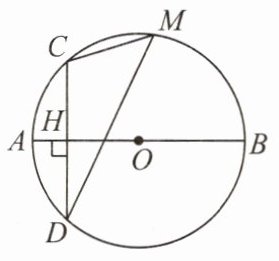

答案:
如图,连接 $OC$,$OD$. $\because AB\perp CD$,$\therefore \angle CHO = 90^{\circ}$,在 $Rt\triangle COH$ 中,$\because OC = r$,$OH = r - 2$,$CH = 4$,$\therefore r^{2}=4^{2}+(r - 2)^{2}$,$\therefore r = 5$. $\because AB\perp CD$,$AB$ 是直径, $\therefore \overset{\frown}{AD}=\overset{\frown}{AC}=\frac{1}{2}\overset{\frown}{CD}$,$\therefore \angle AOC=\frac{1}{2}\angle COD$, $\because \angle CMD=\frac{1}{2}\angle COD$,$\therefore \angle CMD=\angle COA$, $\therefore \sin\angle CMD=\sin\angle COA=\frac{CH}{CO}=\frac{4}{5}$.

如图,连接 $OC$,$OD$. $\because AB\perp CD$,$\therefore \angle CHO = 90^{\circ}$,在 $Rt\triangle COH$ 中,$\because OC = r$,$OH = r - 2$,$CH = 4$,$\therefore r^{2}=4^{2}+(r - 2)^{2}$,$\therefore r = 5$. $\because AB\perp CD$,$AB$ 是直径, $\therefore \overset{\frown}{AD}=\overset{\frown}{AC}=\frac{1}{2}\overset{\frown}{CD}$,$\therefore \angle AOC=\frac{1}{2}\angle COD$, $\because \angle CMD=\frac{1}{2}\angle COD$,$\therefore \angle CMD=\angle COA$, $\therefore \sin\angle CMD=\sin\angle COA=\frac{CH}{CO}=\frac{4}{5}$.

查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


